Bilgi Merkezi
Terminoloji
İhracat Terminolojisi:
- İhracatçı: Başka bir ülkeye mal veya hizmet satan kuruluş.
- İhracat Lisansı: Belirli malların ihracatı için devlet izni.
- İhracat Beyannamesi: İhracat edilen mallar, değerleri ve destinasyonları hakkında detayları içeren belge.
- İhracat Kontrolü: Güvenlik ve uyumluluk için hassas malların ihracatını düzenleyen düzenlemeler.

İthalat Terminolojisi:
- İthalatçı: Başka bir ülkeden mal veya hizmet satın alan kuruluş.
- İthalat Lisansı: Belirli malların ithalatına izin veren ruhsat.
- İthalat Vergisi: Gümrük yetkilileri tarafından ithal edilen mallara uygulanan vergi.
- Gümrük Onayı: İthal edilen malların gümrükten geçiş süreci ve serbest bırakılması.
Belgeler:
- Ticari Fatura: Satıcının, satılan mallar, değerler ve şartları detaylandıran belgesi.
- Konşimento (B/L): Taşıyıcının taşıma sözleşmesi ve mallar için teslimat makbuzu.
- Menşei Şahadetnamesi: Malların menşei ülkesini belgeleyen ve gümrük ile ticaret anlaşmaları için kullanılan belge.
- Yük Taşıma Kompanyası: Bireyler veya şirketler için gönderileri organize eden ve yöneten şirket.
- Gümrük Komisyoncusu: Gümrük işlemleri ve ithalat/ihracat düzenlemeleriyle uyumluluk konusunda uzmanlaşmış lisanslı temsilci.
- Taşıyıcı: Malları hava, deniz, kara veya demir yoluyla taşıyan şirket veya birey.
Taşıma Türleri
Hava Taşımacılığı:
Uzun mesafelerde en hızlı yol. Bozulabilir mallar ve acil gönderiler için uygundur. Küresel bağlantı sağlar.
Deniz Taşımacılığı:
Büyük hacimli ve ağır yükler için maliyet-etkin. Uzun mesafelerde acil olmayan gönderiler için ideal. Hava koşulları ve liman sıkışıklığına bağlıdır.
Kara Taşımacılığı:
Kapıdan kapıya esnek hizmet. Kısa ve orta mesafeler için uygundur. Ulaşılması zor bölgelerde erişilebilir.
Demir Yolu Taşımacılığı:
Kara üzerinde uzun mesafelerde maliyet-etkin. Kara taşımacılığına kıyasla daha düşük emisyonlar. Güvenilir programlar.

Konteyner Türleri
Standart 20-Foot Kuru Konteyner:
Genel kargo taşımacılığı için en yaygın kullanılan tür. Kapasite ve manevra kabiliyeti açısından dengeli. Yaklaşık 20 feet uzunluğunda, 8 feet genişliğinde ve 8.5 feet yüksekliğinde. Yaklaşık 33 metreküp (1,170 cubic feet) kargo kapasitesi.
Standart 40-Foot Kuru Konteyner:
Uluslararası gönderilerde daha büyük kapasitesi ile yaygın olarak kullanılır. Geniş bir kargo yelpazesi için uygundur. Yaklaşık 40 feet uzunluğunda, 8 feet genişliğinde ve 8.5 feet yüksekliğinde. Yaklaşık 67 metreküp (2,390 cubic feet) kargo kapasitesi.
Incoterms
Incoterms, Uluslararası Ticaret Terimleri’nin kısaltmasıdır ve Uluslararası Ticaret Odası (ICC) tarafından yayınlanan standart terimlerdir. Bu terimler, uluslararası ticari işlemlerde alıcıların ve satıcıların teslimat, risk transferi ve maliyet paylaşımı hak ve yükümlülüklerini tanımlar.
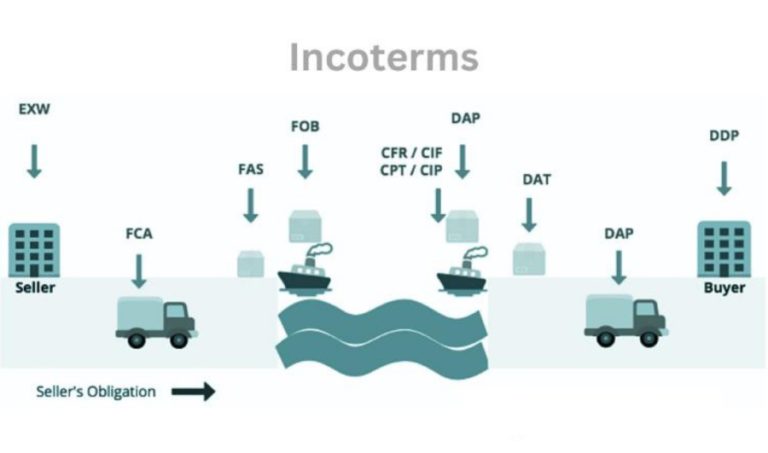
- EXW (Ex Works): Satıcı, malları kendi tesislerinde mevcut kılar. Alıcı, tüm maliyet ve riskleri bu noktadan itibaren üstlenir.
- FCA (Free Carrier): Satıcı, malları alıcının belirlediği taşıyıcıya teslim eder. Alıcı, sonraki tüm maliyet ve riskleri üstlenir.
- CPT (Carriage Paid To): Satıcı, taşıma ücretini belirtilen destinasyona kadar öder. Risk, taşıyıcıya teslim anında alıcıya geçer.
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To): Satıcı, taşıma ve sigorta ücretlerini belirtilen destinasyona kadar öder. Risk, taşıyıcıya teslim anında alıcıya geçer.
- DAP (Delivered at Place): Satıcı, malları belirtilen varış yerinde alıcının kullanımına sunar. Satıcı, malları getirirken tüm riskleri üstlenir.
- DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded): Satıcı, malları boşaltılmış olarak belirtilen varış yerinde alıcının kullanımına sunar. Satıcı, malları getirirken tüm riskleri üstlenir.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): Satıcı, malları belirtilen varış yerinde alıcının kullanımına sunar, ithalat için gümrük işlemlerini tamamlar ve tüm vergi ve gümrük formalitelerini yerine getirir.
- FAS (Free Alongside Ship): Satıcı, malları belirlenen limanda geminin yanına koyar. Risk, malların geminin yanına konmasıyla alıcıya geçer.
- FOB (Free on Board): Satıcı, malları belirlenen limanda gemiye yükler. Risk, malların gemiye yüklenmesiyle alıcıya geçer.
- CFR (Cost and Freight): Satıcı, malları gemiye yükler veya yüklenmiş olarak temin eder. Risk, malların gemiye yüklenmesiyle alıcıya geçer.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): Satıcı, malları gemiye yükler veya yüklenmiş olarak temin eder. Risk, malların gemiye yüklenmesiyle alıcıya geçer.
Tehlikeli Mal Kodları

Hazmat Placards and UN Numbers: What You Need to Know
Have you ever seen a truck, railcar, container or large tanks at a tank farm and wondered what types of chemicals it was transporting or storing? The answer can be found in its UN numbers and hazmat placards.
What Are UN Numbers
Located on the back or sides of trailers or other containers, UN numbers (or UN IDs) are four-digit numbers ranging from 0004-3534 that identify dangerous goods or hazardous substances — such as explosives, flammable liquids, or toxic substances — in the framework of international transport.
These numbers are assigned by the United Nations (UN) Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, and must be listed on the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) of each shipment. (Goods that aren’t classified or regulated by the UN are given four-digit North American (NA) numbers ranging from 8000-9279. These numbers are designated by the United States Department of Transportation (DOT).)
What Are Hazmat Placards?
In addition to a UN number, the DOT requires cargo to carry Hazmat placards that help shippers determine its class, division, and compatibility group.
Similar to road or construction signs, these diamond-shaped hazmat placards alert the public that potentially hazardous materials are being hauled, as well as inform emergency responders which chemicals are present in case of an accident. Even if members of the public or first responders are unaware of exactly which materials are on board, the presence of hazmat placards lets them know that they should proceed with caution.
With rare exceptions, companies that transport hazardous materials without the use of DOT hazmat placards are at risk for stiff fines and other penalties.
UN Hazmat Sign Components and Classifications
It’s vital that anyone who works with or around hazardous materials can properly identify the various aspects of each hazmat placard, as well as the various classifications that each one represents.
CLASSIFICATIONS
Hazmat warning placards are broken down into nine different classifications, along with their divisions. Each class number is found at the bottom of the sign, while the division number can be found in the middle.
Class 1 — Explosive Materials
1.1: Products with the potential to create a mass explosion
1.2: Products with the potential to create a projectile hazard
1.3: Products with the potential to create a fire or minor blast
1.4: Products with no significant risk of creating a blast
1.5: Products considered very insensitive that are used as blasting agents
1.6: Products considered extremely insensitive with no risk to create a mass explosion
Class 2 — Gases
2.1: Flammable gases
2.2: Nonflammable gases
2.3: Toxic gases
Class 3 — Flammable and Combustible Liquids
Class 4 — Flammable Materials
4.1: Flammable solids
4.2: Spontaneously combustible
4.3: Dangerous when wet
Class 5 — Oxidizer and Organic Peroxide
5.1: Oxidizing substances
5.2: Organic peroxides
Class 6 — Poisons
6.1: Toxic substances
6.2: Infectious substances
Class 7 — Radioactive Materials
Class 8 — Corrosive Materials
Class 9 — Miscellaneous Materials
COMPONENTS
Each hazmat sign has up to six main parts:
-
- Hazard classification number — See below.
- UN/NA number — See above.
- Compatibility letters — Some placards include the letters A-S, which let shippers and carriers know which explosive materials can be loaded together onto a trailer.
- Color — Other than classification numbers, hazmat placards are most easily identified by their different colors.
- Orange represents explosive materials, including products like dynamite, ammunition, or fireworks.
- Red represents flammable goods like gasoline, rubbing alcohol, paint, or acetone.
- Green signs signify non-flammable substances like compressed or liquefied gases.
- Yellow indicates the transport of oxidizers — like ammonium nitrate, potassium nitrate, or nitric acid — that are likely to combust when mixed with oxygen.
- White represents poisonous and bio-hazardous substances like dyes, aerosols, acids, and medical waste.
- Blue signifies materials that can become flammable when combined with water, like sodium, calcium, and potassium.
- A half red and white sign indicates the presence of substances that can ignite when exposed to air, like aluminum and lithium alkyls or white phosphorous.
- Red and white stripes indicate flammable solids such as matches and magnesium.
- Red and yellow indicate organic peroxides that can ignite or explode, including methyl ethyl ketone peroxide and benzoyl peroxide.
- Yellow and white represent radioactive substances often found in medical equipment.
- Half white and half black indicates corrosive materials that can irritate and harm the skin, including batteries, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and sodium hydroxide.
- White with black vertical stripes denote various dangerous goods, including nonclassified, environmentally hazardous substances like asbestos and dry ice.
- Words — Depending on the contents of each container, its hazmat placard is labeled with various terms like “Spontaneously Combustible,” “Explosive,” “Nonflammable Gas,” “Oxygen,” “Poison,” “Flammable,” and others.
- Graphics — Different hazmat placards feature illustrations to reinforce the danger of their contents. For example, placards for toxic materials include an image of a skull and crossbones, while signs for radioactive materials include a radiation symbol consisting of three blades surrounding a small circle.
Rules for Placement
According to federal regulations, each freight container, railcar, transport vehicle, or other vessel carrying hazardous materials must display placards on each side and each end. Regulations also state that placards on railcars and transport vehicles must be clearly visible from the direction they face unless they are obscured when coupled with another railcar or transport vehicle.
In all, carriers must display at least four placards in areas where the view isn’t obstructed. Some carriers add extra signs on each side of the truck cab for additional visibility.
İhracat Ürün Kodları
Export product codes can vary depending on the country and the specific classification system used.
Here are some common types of export product codes and their descriptions:

Harmonize Sistem (HS) Kodu:
Malların küresel olarak sınıflandırıldığı bir sistem. Detaylar için buraya bakabilirsiniz.
Daha fazla bilgi için lütfen bağlantıya tıklayın https://www.wcoomd.org
Schedule B Numarası (ABD):
ABD’den yapılan ihracatlar için kullanılan kod. Detaylar için buraya bakabilirsiniz.
Daha fazla bilgi için lütfen bağlantıya tıklayın https://www.wcoomd.org
Gümrük Tarife Kodu (AB):
Avrupa Birliği ülkelerinden yapılan ihracatlar için kullanılan kod. Detaylar için buraya bakabilirsiniz.
Daha fazla bilgi için lütfen bağlantıya tıklayın https://taxation-customs.ec.europa.eu
Ticaret Kodu (Birleşik Krallık):
Daha fazla bilgi için lütfen bağlantıya tıklayın https://www.gov.uk/trade-tariff
